The Hidden Art of Car Restoration: Reviving Automotive Treasures
The world beneath the hood of a classic automobile holds stories untold. Car restoration represents more than mechanical repairs; it embodies preservation of automotive heritage and craftsmanship that defined generations. Enthusiasts worldwide dedicate countless hours to breathing new life into forgotten vehicles, transforming rust-laden shells into gleaming masterpieces. This meticulous process combines technical expertise, historical research, and artistic vision. The passion driving restorers transcends simple appreciation—it reflects a commitment to keeping automotive history alive through skilled hands and determined hearts.

Understanding the Restoration Philosophy
Car restoration exists on a spectrum ranging from preservation to modification. Purists advocate for maintaining historical accuracy, using period-correct parts and techniques to return vehicles to their original factory specifications. This approach requires extensive research, documentation collection, and sometimes global searches for authentic components. Alternatively, restomodding combines classic aesthetics with modern performance upgrades, creating vehicles with vintage charm and contemporary reliability. Both philosophies share a common foundation: respect for automotive heritage while acknowledging that each restoration tells a unique story reflecting the relationship between car and restorer. The most successful projects balance historical significance with personal vision, creating automotive treasures that honor both past and present.
The Crucial First Steps: Assessment and Planning
Every successful restoration begins with comprehensive assessment. Experienced restorers document each vehicle thoroughly before disassembly, taking hundreds of photographs and creating detailed notes about component conditions and relationships. This documentation proves invaluable during reassembly months or years later. Next comes creating a restoration plan encompassing timeline, budget, parts sourcing strategy, and technical approach. This planning phase often reveals hidden challenges—floors concealed by carpets may hide severe rust, chrome seemingly intact might require complete replating, and engines running smoothly could secretly harbor internal damage. Professional restorers understand that realistic expectations during this phase prevent costly surprises later. The planning document becomes a living guide, evolving as the project progresses and new information emerges from deep within the vehicle.
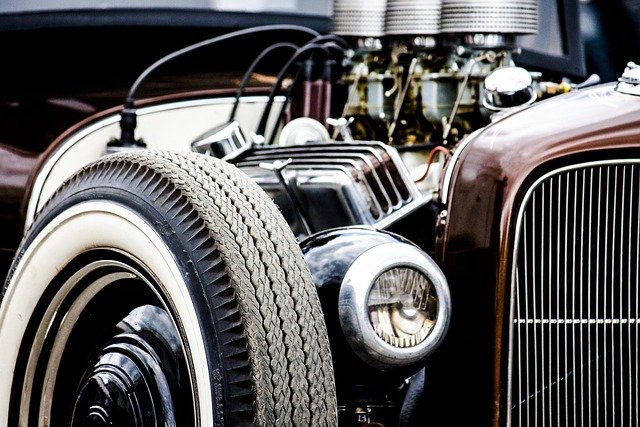
Bodywork: The Most Challenging Aspect
Bodywork represents the most technically demanding and time-consuming aspect of restoration. Metal restoration requires specialized skills including panel beating, welding, lead work, and fabrication techniques that modern manufacturers have largely abandoned. Environmental factors and previous repair attempts often complicate matters further. Rust removal and prevention demands methodical approaches beyond simple grinding—proper metal treatment, primer application, and sealing techniques determine whether restoration efforts last decades or deteriorate within years. Paint preparation requires equal precision, with multiple stages of progressive sanding to achieve mirror-like surfaces. The application of modern paints on vintage vehicles presents unique challenges, as contemporary formulations behave differently than original lacquers and enamels. Master restorers develop specialized techniques combining traditional craftsmanship with modern materials to achieve results that honor original appearances while providing superior protection against environmental elements.
The Mechanical Rebirth
Engine and drivetrain restoration represents a delicate balance between historical authenticity and practical functionality. While visual correctness matters for show vehicles, reliability and usability define successful projects meant for regular driving. The restoration process typically begins with complete disassembly and inspection, revealing wear patterns that indicate underlying problems potentially invisible from external examination. Machine shops play crucial roles in this phase, handling precision operations like cylinder boring, crankshaft grinding, and valve seat reconditioning. Decisions regarding upgrades require careful consideration—subtle improvements like modern valve seals or updated bearing materials can enhance reliability without compromising authenticity, while more substantial changes like electronic ignition systems or overdrive transmissions change the driving character but improve usability. The most successful mechanical restorations maintain period-correct appearance while incorporating hidden enhancements that address known design weaknesses or improve safety without betraying the vehicle’s historical integrity.
Interior Restoration: Where Art Meets Function
Interior restoration combines craftsmanship, material science, and historical research. Original upholstery materials often differ significantly from modern counterparts—vinyl formulations, leather tanning methods, and fabric weaving techniques have evolved substantially over decades. Skilled trimmers replicate patterns and textures using combinations of vintage and contemporary materials to achieve historically accurate appearances with improved durability. Dashboard restoration presents unique challenges, requiring specialized knowledge of gauge restoration, wood veneering, and chrome refinishing. The most challenging aspects often involve reproducing plastic components that have deteriorated or cracked over time—techniques ranging from silicone molding to 3D scanning help recreate these irreplaceable parts. Climate control systems present particular difficulties, as restorers balance period correctness against functioning cooling and heating capabilities suitable for modern driving conditions. Successful interior restoration creates environments that transport occupants through time while providing comfort and functionality that meet contemporary expectations.
Documentation and Authentication
Professional restoration documentation provides both historical record and value protection. Comprehensive photographic archives, receipts, certificates of authenticity, and build documentation substantiate restoration quality and historical accuracy. For rare or significant vehicles, establishing provenance through research, historical records, and factory documentation can substantially impact value. Many restoration projects involve detective work—tracing vehicle histories through previous owners, discovering original factory specifications, and verifying numbers matching status. Organizations like classic car clubs, manufacturer archives, and restoration associations provide valuable resources for authenticating vehicles and establishing correct specifications. This documentation process serves multiple purposes: guiding accurate restoration decisions, proving vehicle authenticity for future owners, and preserving automotive history that might otherwise be lost to time.
The Future of Classical Restoration
Traditional restoration faces evolving challenges as vehicles from different eras require new approaches and skills. As collectible cars from the 1980s and 1990s gain appreciation, restorers encounter unfamiliar materials and technologies—electronic fuel injection, digital dashboards, and complex emissions equipment demand specialized knowledge beyond traditional mechanical skills. Environmental regulations increasingly impact restoration practices, with restrictions on materials and processes once common in automotive refinishing. Parts availability presents growing concerns, with fewer manufacturers supporting older vehicles through reproduction components. However, technological advancements offer new possibilities through 3D printing, computer-aided design, and material science innovations that enable recreation of previously irreplaceable components. The restoration community continues adapting, with knowledge sharing through online forums, specialized training programs, and apprenticeship opportunities ensuring these specialized skills continue into future generations. Despite these challenges, the fundamental drive to preserve automotive history remains unwavering, ensuring this blend of art and engineering continues evolving while maintaining its core purpose.